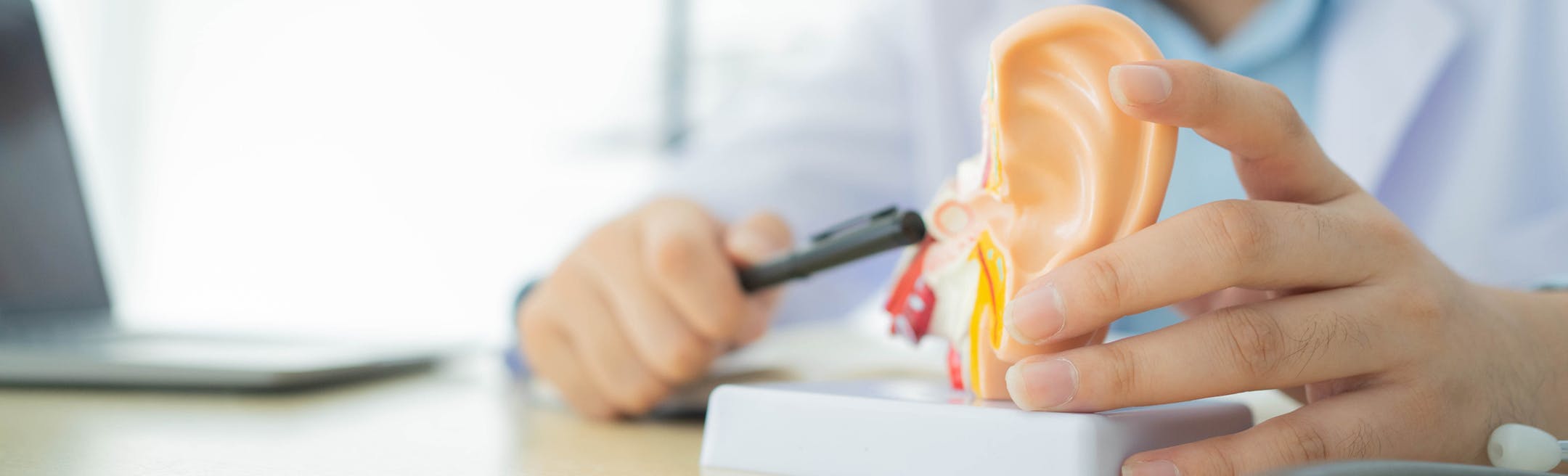
A ruptured, or perforated, eardrum is a tear in the thin membrane that separates the inner ear from the middle ear. The eardrum is an important part of how we hear, as it is instrumental in the process of converting a sound wave that enters the ear into an electrical signal that gets sent to the brain. The eardrum also works as a barrier to keep water and other objects from entering the middle ear.
Symptoms
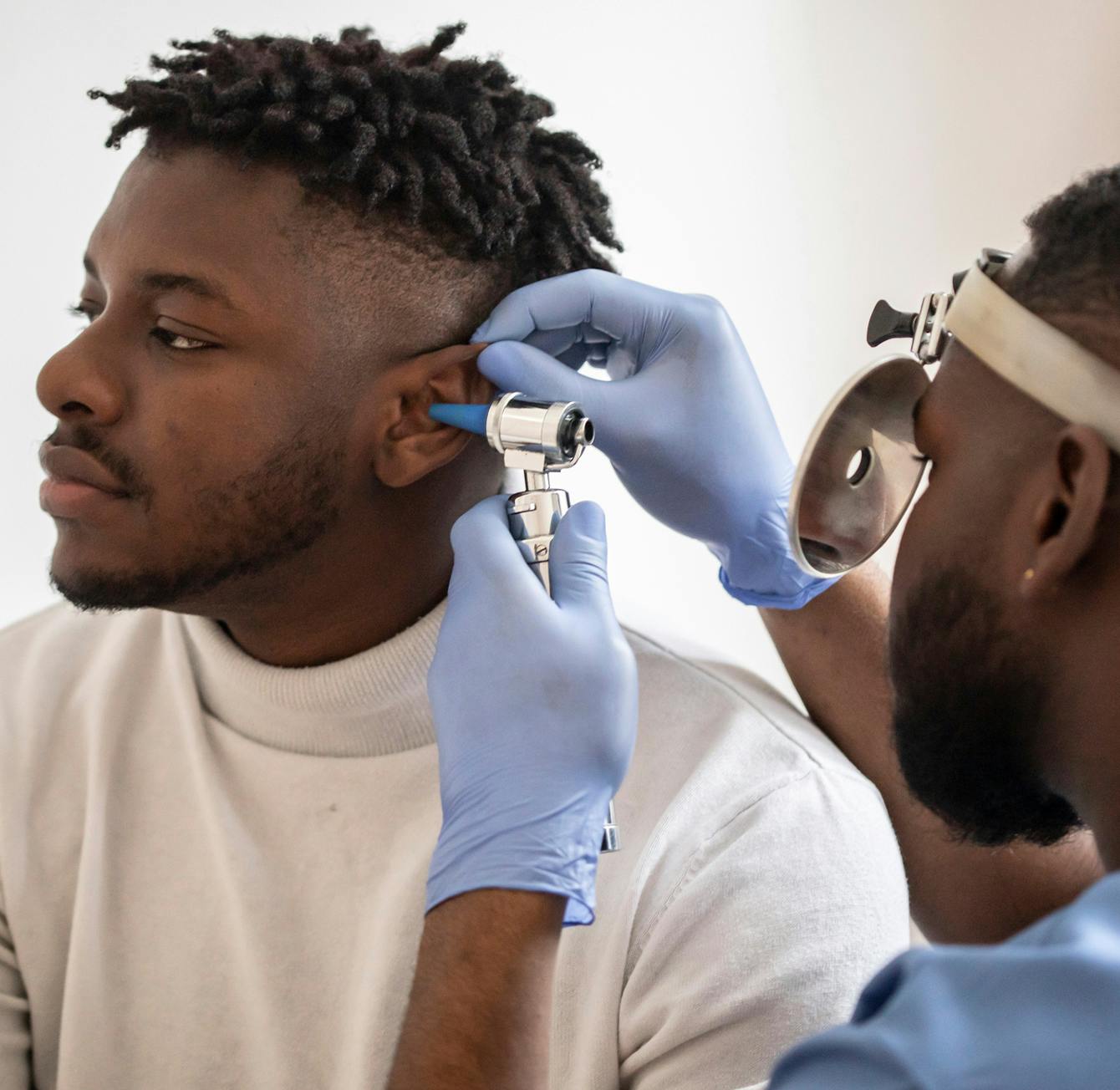
The symptoms experienced by those with a ruptured eardrum can vary. The most common symptoms are a sudden sharp pain, drainage from the ear, buzzing or hearing loss. Some may not feel anything at all. If you experience any of these symptoms, contact your doctor as soon as possible. To confirm the diagnosis, your doctor will use an otoscope, a device with a light on the end, to look inside your ear. Usually, the hole or tear is visible. In order to test if the ruptured eardrum has affected your hearing, your doctor will also perform some hearing tests.